Cloud Broker - Essentials for a Cloud Service Brokerage Platform
Cloud technology has become exponentially accepted for companies all over the world, providing a Cloud Service Brokerage platform for them to run their sensitive and critical operations, therefore cloud services are now more than ever a very integral part of the ICT infrastructures exploited by companies from many different industries.
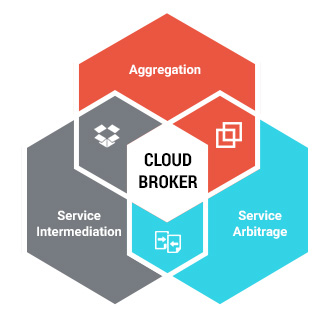
According to Gartner, Cloud Service Brokerage (CSB) is an ICT role and business model in which a company or other entity adds value to one or more (public or private) cloud services on behalf of one or more consumers of that service via three primary roles including;
- Aggregation: this involves combining and integrating multiple services, examples are; data integration, safeguarding process integrity and ensuring data portability between the cloud customer and the various cloud services providers.
- Service Intermediation: this is the provision of value-added services or basically improving a capability without actually providing any of the cloud services itself. These services may include identity and access management, security management and reporting, or supervision on pricing and billing.
- Service Arbitrage: Some cloud broker services providers are not directly involved in cloud customer contact, but rather enable other cloud broker services providers to provide their brokerage services. Examples of these cloud brokerage enablers are providers of cloud aggregation platforms or other (software) technology that enable aggregation providers to combine various cloud services into one or more aggregated cloud services to the cloud customer.